How to Move Your Root File System from eMMC Flash to an M.2 SSD
November 13, 2024 1002
How to Move Your Root File System from eMMC Flash to an M.2 SSD
What You Will Learn:
- How to format the M.2 device as ext4.
- How to copy the root file system.
- How to assign the M.2 device as the new root file system.
When using a Jetson module, moving your root file system from eMMC flash to SSD storage on an M.2 slot can significantly improve boot time and performance. In this tutorial, we’ll walk you through each step to transfer your root file system from the eMMC flash to an M.2 SSD.
In previous versions, mounting the SSD through a service introduced a delay because the eMMC-mounted root had to be loaded first. By making the SSD your primary root file system, the Jetson module will boot directly from it. Note: The Jetson module won’t boot without the SSD until the extlinux.conf file is updated. To avoid issues, make a backup of your system before proceeding.

The sudo jetson_clocks command allocates maximum resources, and gnome-disks opens the GNOME Disks application, allowing you to manage storage devices.
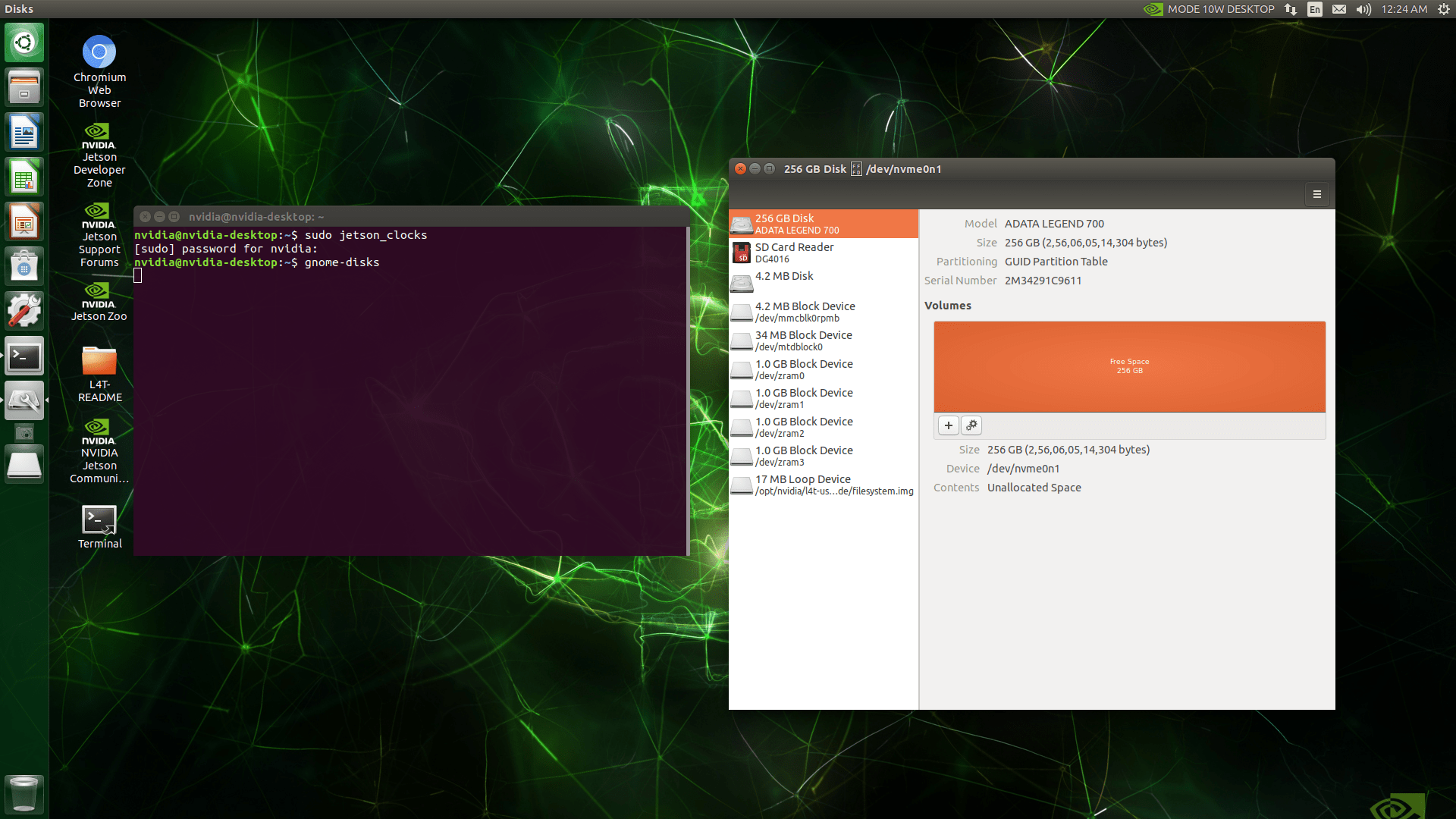

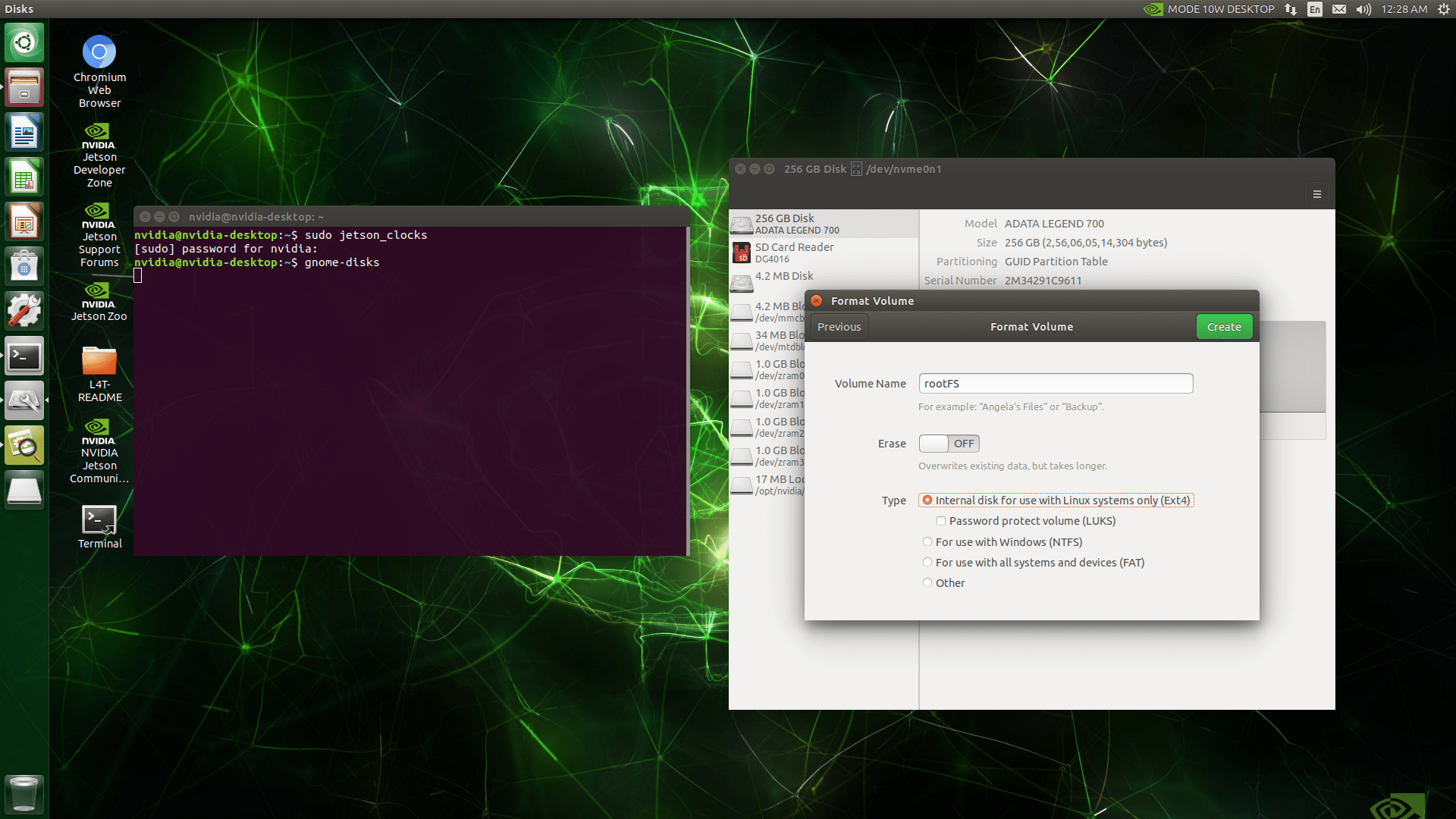
In GNOME Disks, select the SSD and format the entire disk.
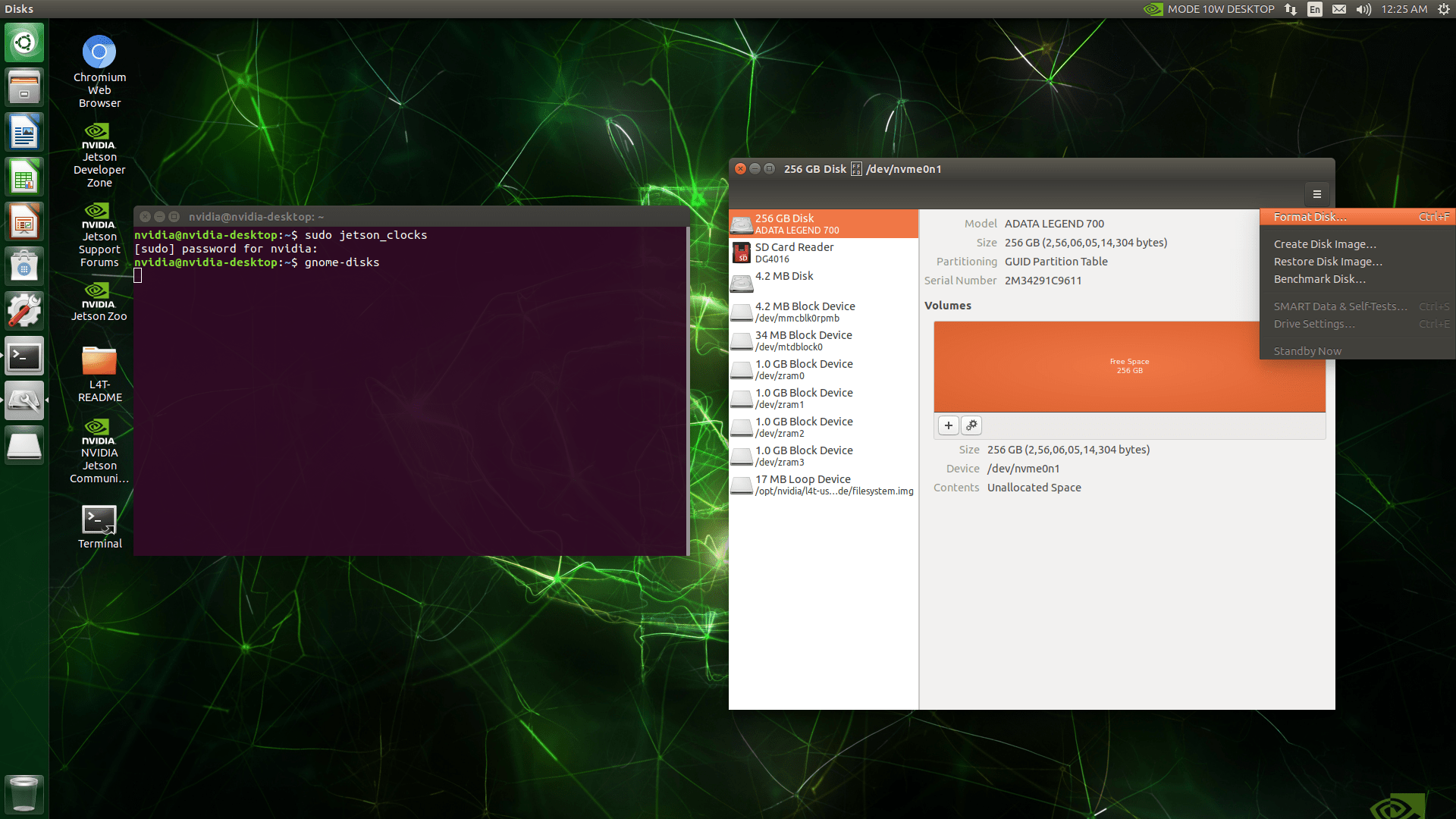

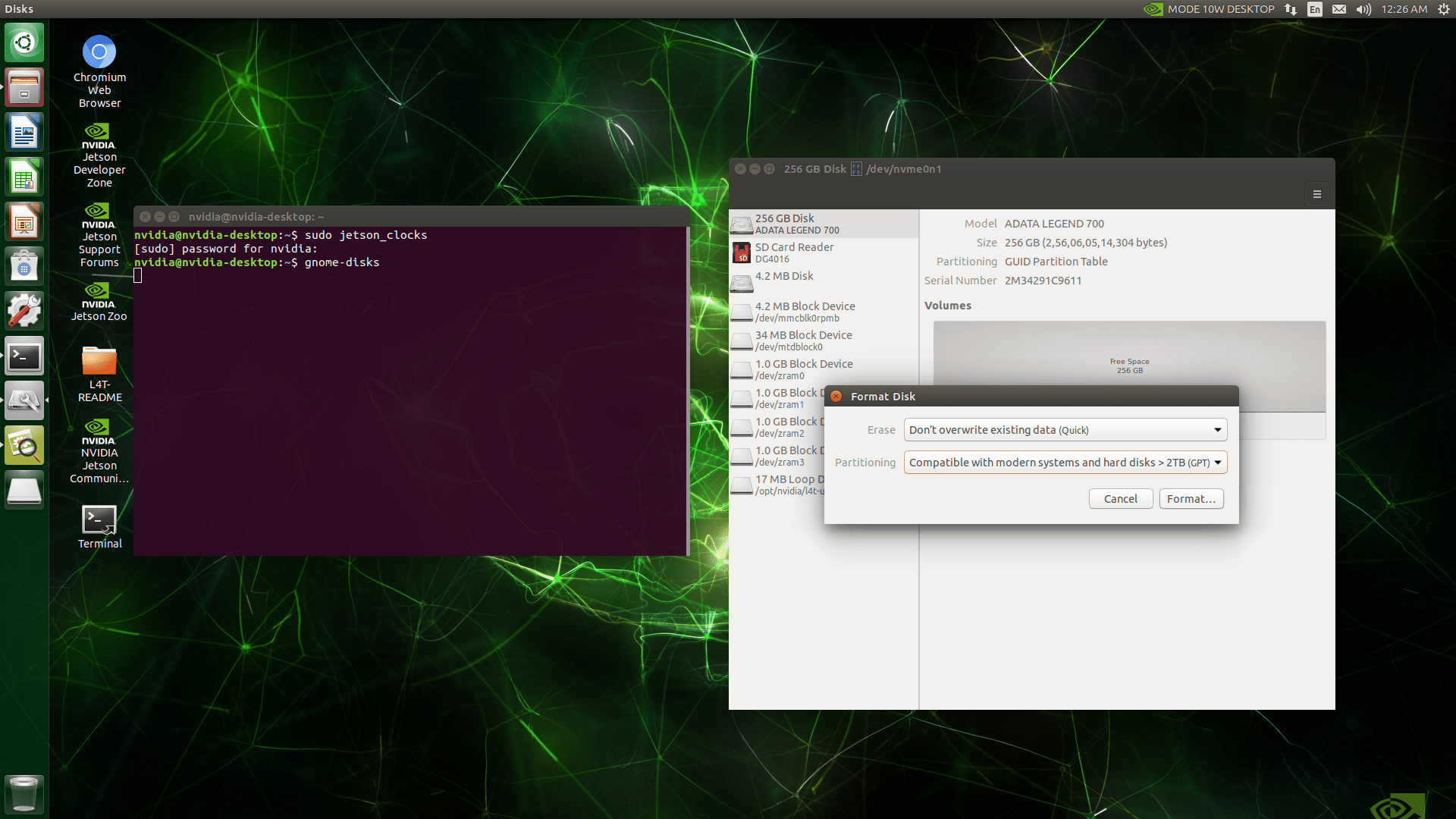

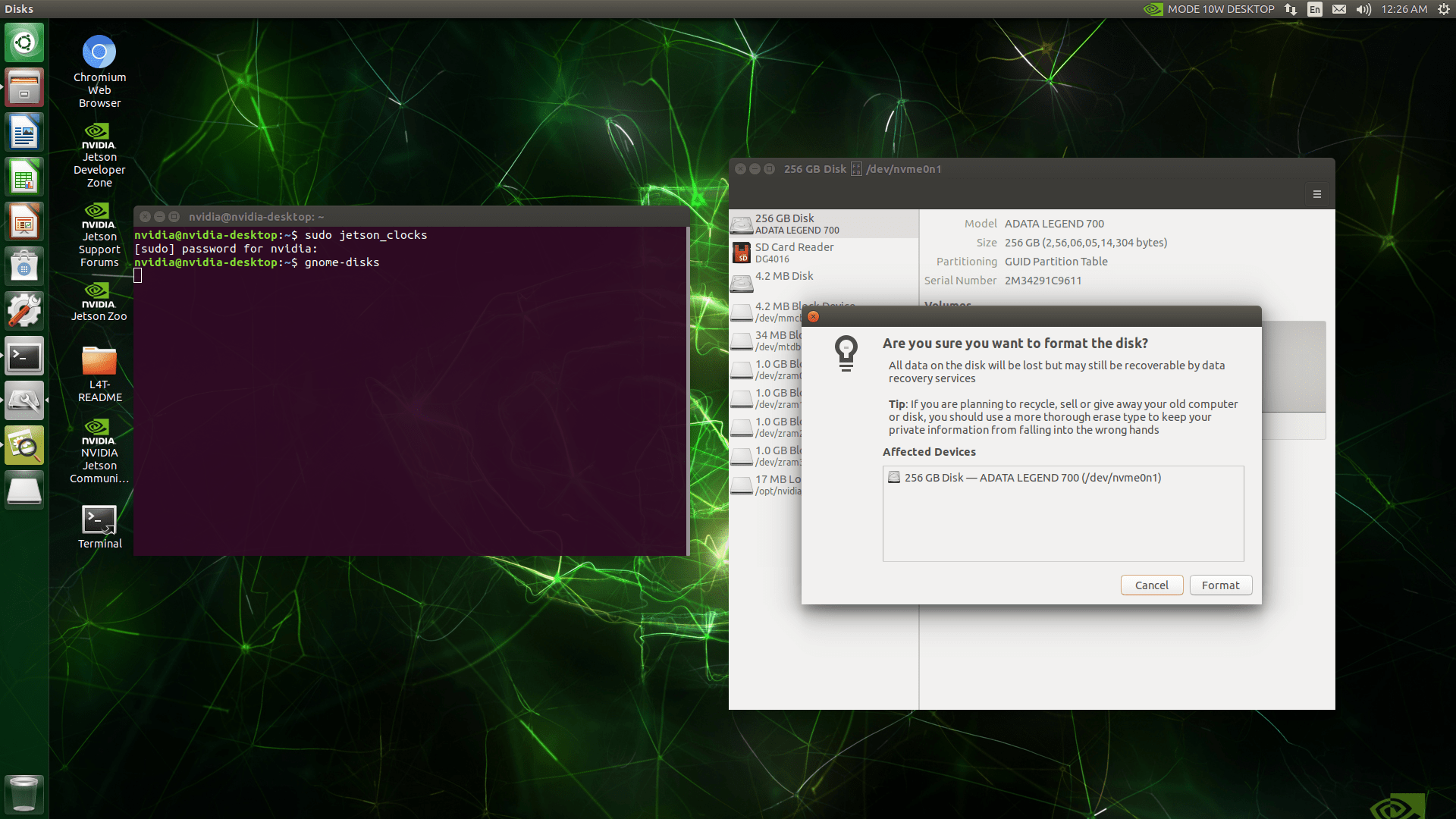

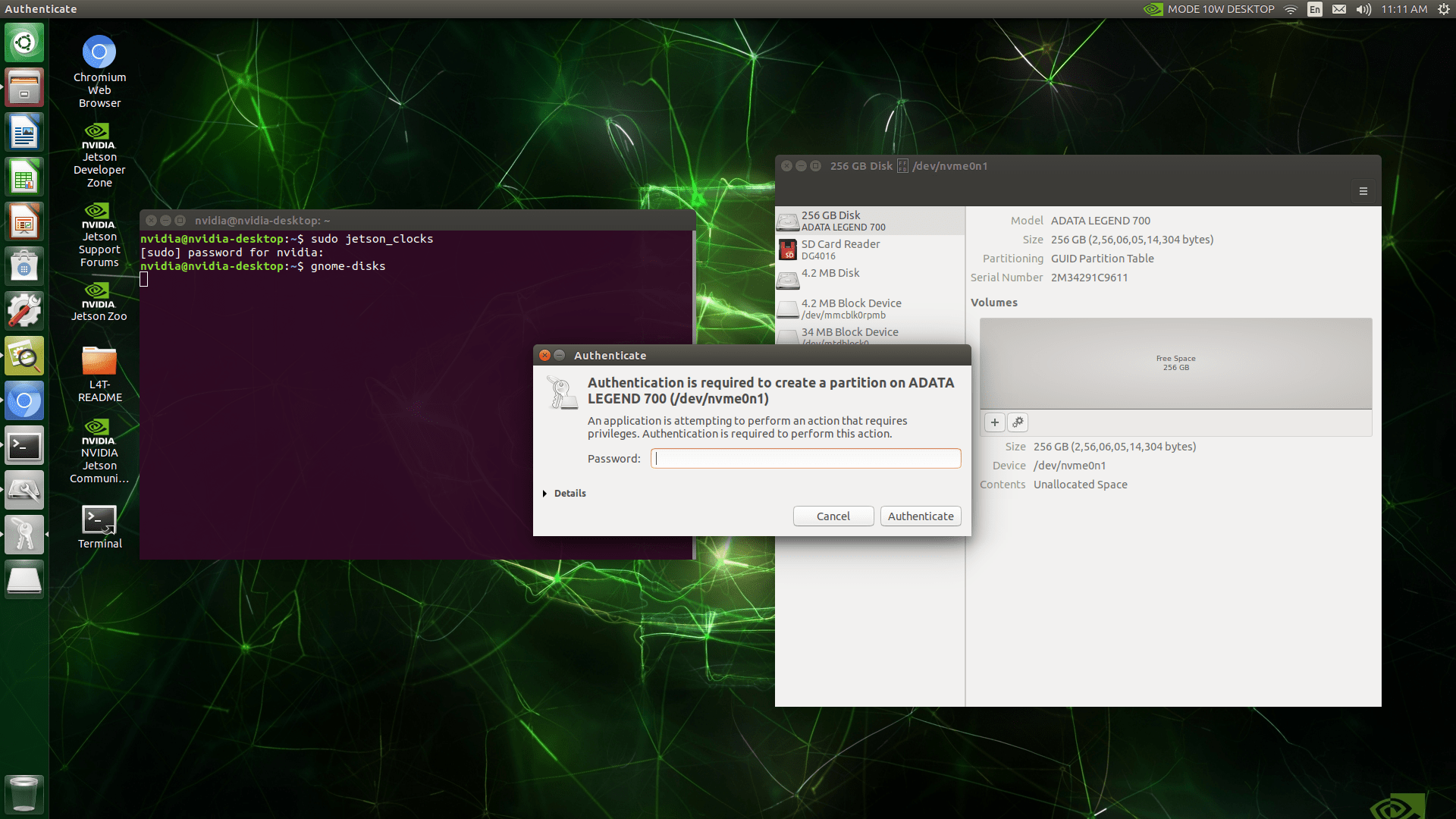

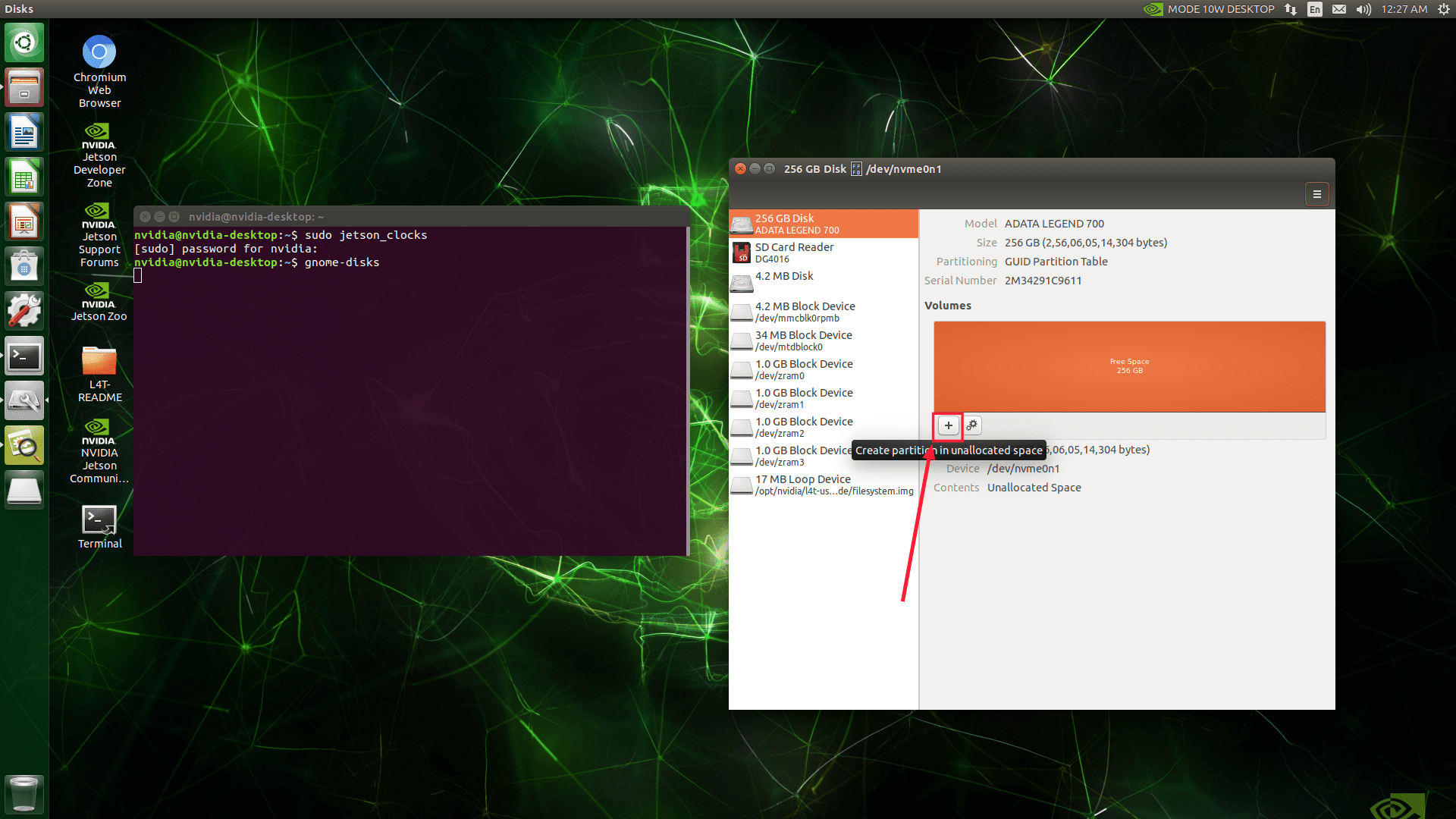

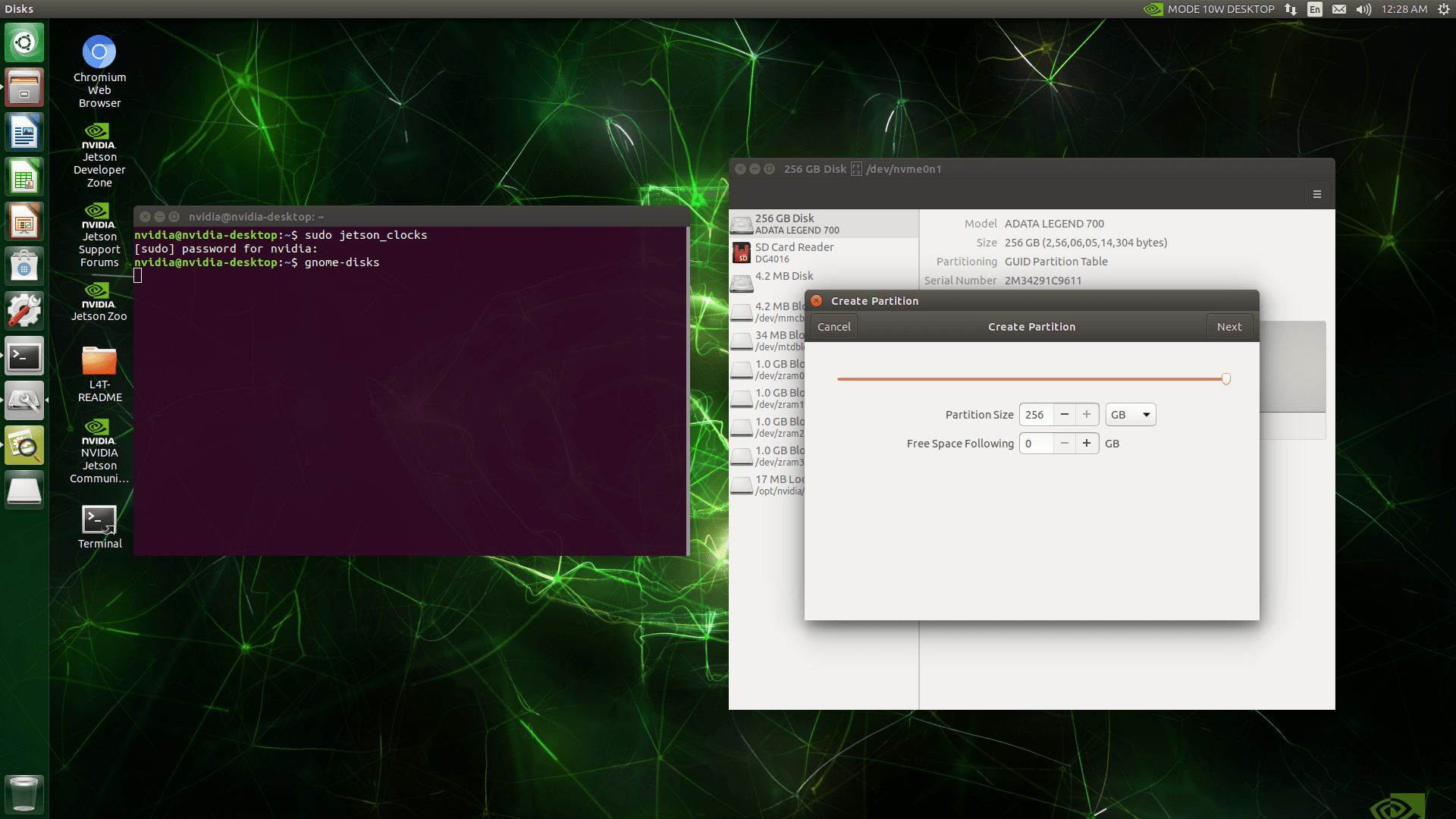

Create a new partition on the SSD and format it as ext4. Ensure the partition size is at least as large as the current root file system.

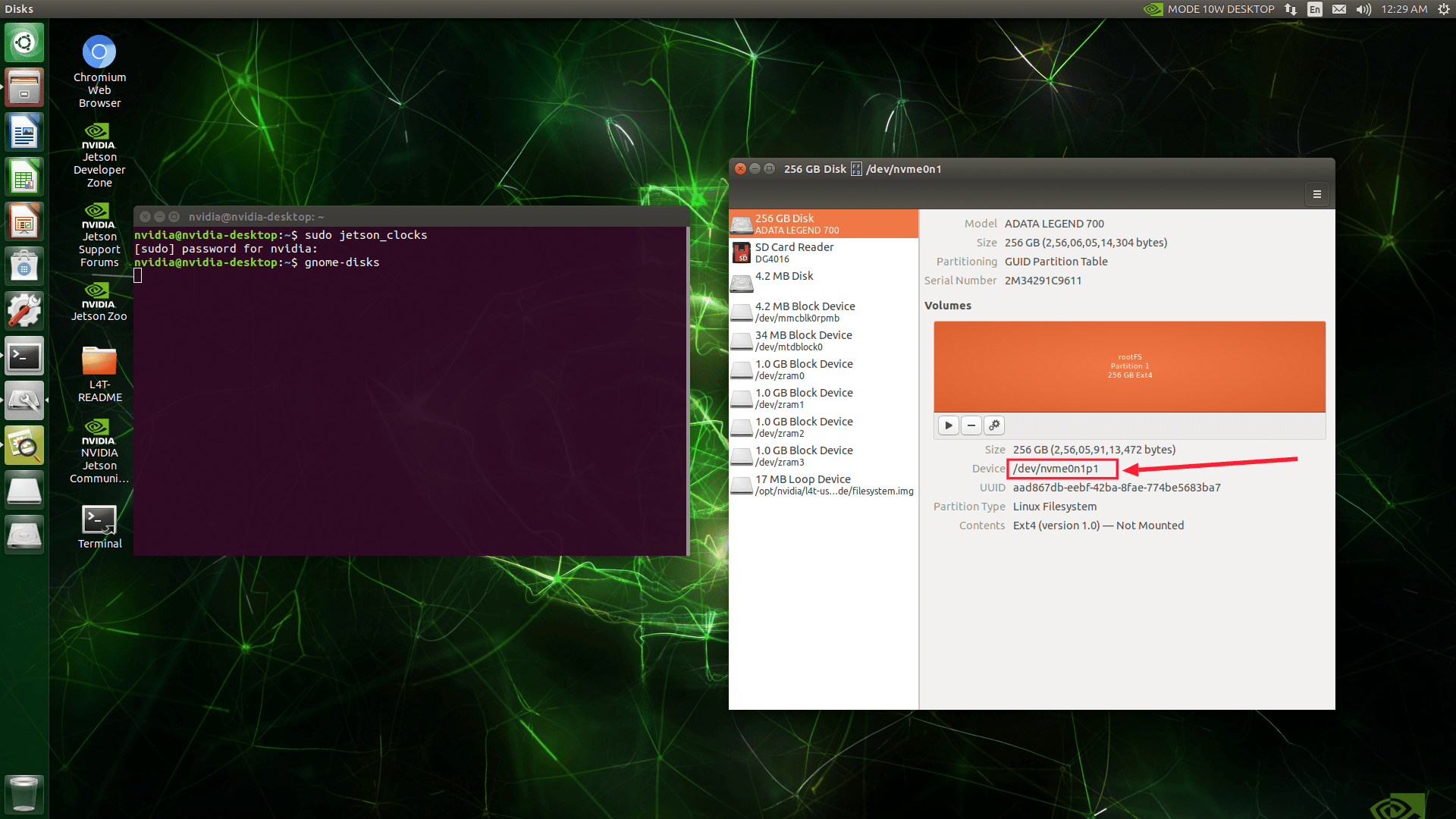
Take note of the SSD partition’s name, typically something like /dev/nvme0n1p1.

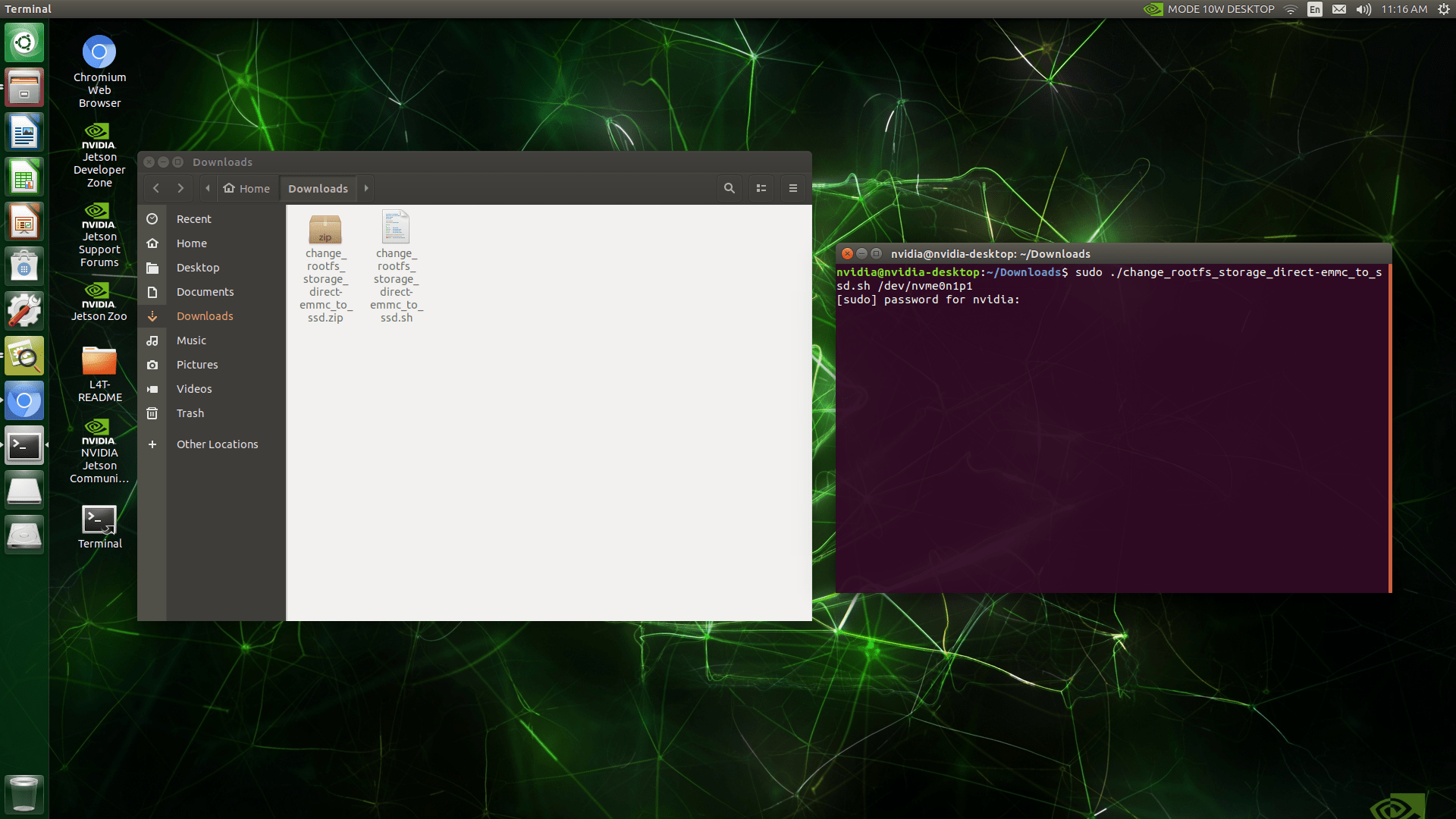
Step 2: Copy the Root File System to the SSD
Download the script file from here and extract it. Then, run it with this command below:
In the terminal, run the script with this command (replace {EXTERNAL_STORAGE} with the path of your SSD partition):
sudo ./change_rootfs_storage_direct-emmc_to_ssd.sh {EXTERNAL_STORAGE}
This script copies the entire root file system to the SSD and updates the root path. Wait for the process to complete.

A few times later, the whole file system copied and the root path changed.
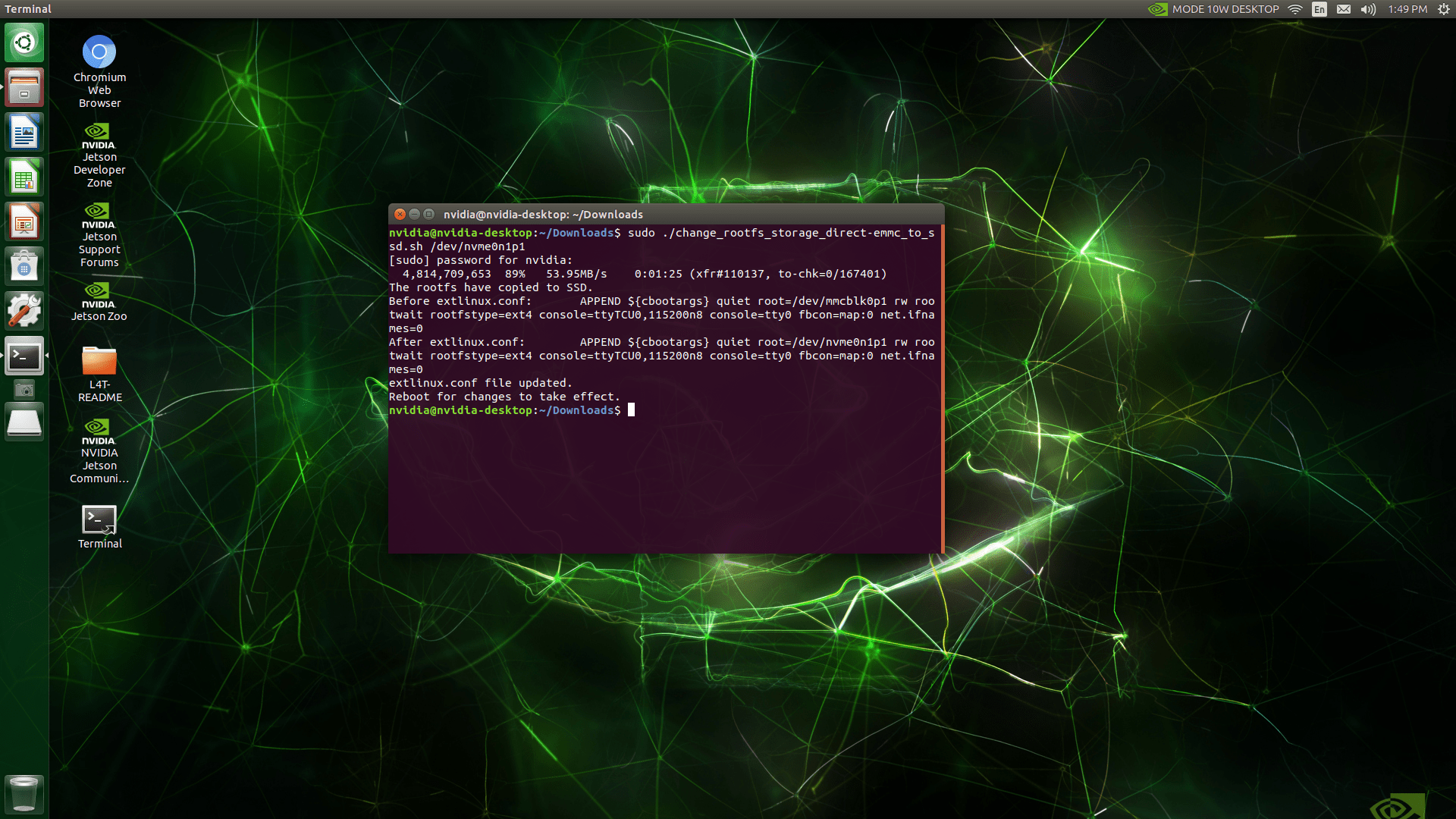

Once finished, reboot your device. Reboot it and check the Root File System copied successfully.
Step 3: Verify the Root File System Assignment
After rebooting, open a terminal and type:
Confirm that the root file system is now mounted from the SSD.
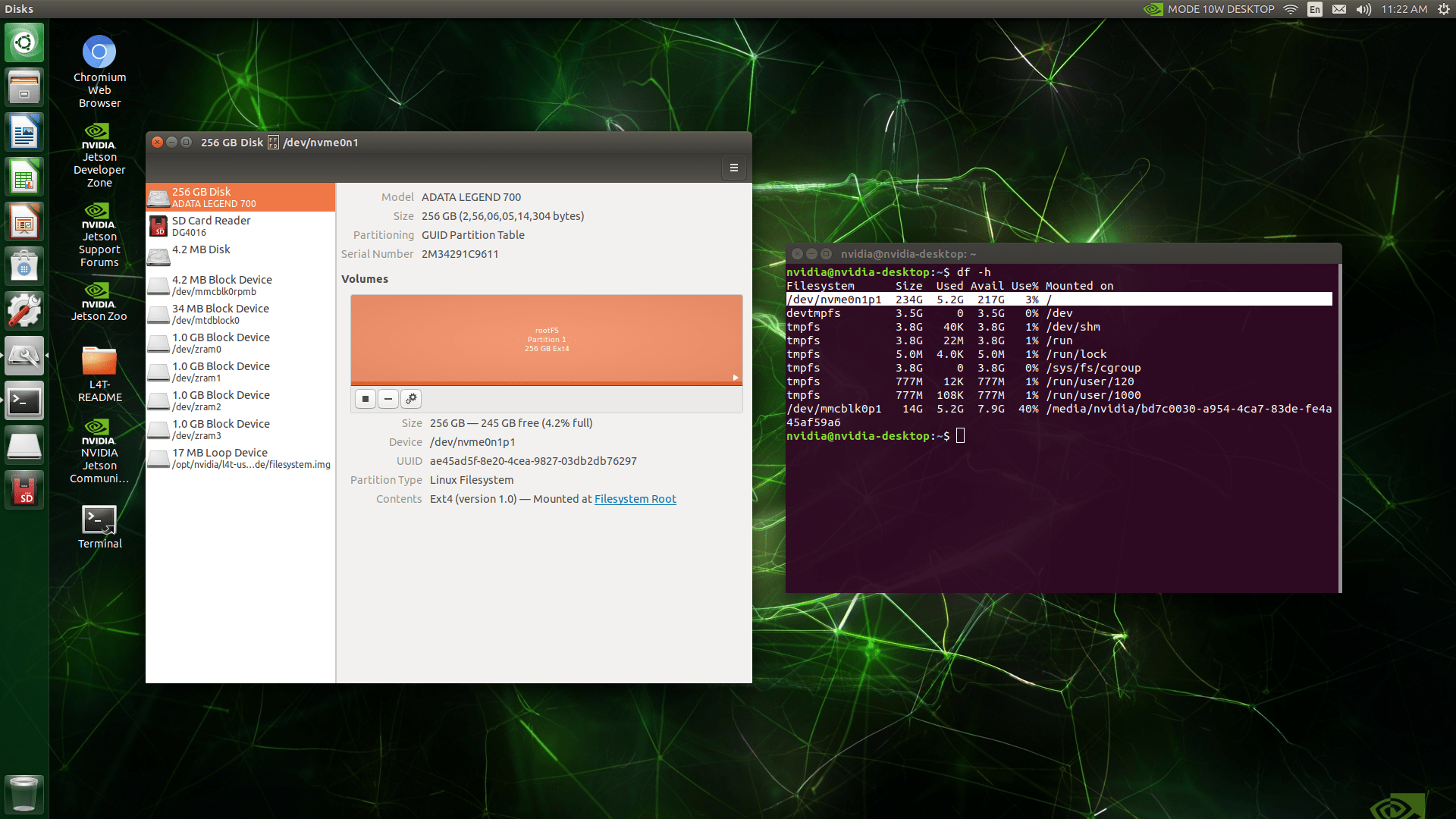

By following these steps, your Jetson module will boot directly from the SSD, giving you faster boot times and improved performance.
Thanks for following along—enjoy your optimized setup!
Special thanks to our fellow Engineer and Colleague -Kishan &